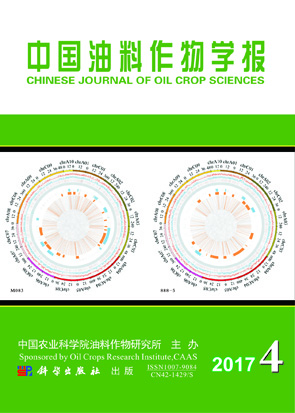
To facilitate fine mapping and gene cloning, variations of whole genome and dense QTL regions of Brassica napus were investigated by sequencing 2 parents (M083 and 888-5, with significant differences in plant height, branch numbers, flowering time and resistance to Sclerotinia disease) and their RIL (recombinant inbred line) population. Results showed that M083 and 888-5 genomes had large amount of variants, including 1 941 397 and 2 046 009 SNPs, 410 961 and 428 572 InDels, 90 384 and 88 456 SVs, 46 655 and 46 008 CNVs respectively. Chromosome A02 was analyzed in detail for its dense QTLs on flowering time, Sclerotinia resistance and plant height. At a QTL dense region (6.4-6.9Mb) of 0-8.5Mb genome, the 2 parents had converse trends in distribution of SNPs and InDels. Segmental loss had hotspot regions in the same 2 regions of the parents with high frequency, and one of them contained the dense QTL region. Inversion distributed unevenly with hotspots in different regions in the parents. It had no overlap with QTL region. The possible causal relationship between hotspots of genomic variation (SNPs, InDels and SVs except for inversion) and dense QTL region might refine QTL mapping and cloning.
Auxin is one of the most important hormones regulating plant growth and development, and TIR1/AFBs are the main auxin receptors involved in auxin response and auxin signaling pathway. In this study, we analyzed TIR1/AFB family members in soybean. According to the phylogenetic analysis of auxin receptors between Arabidopsis and soybean, the soybean TIR1/AFB genes could be subdivided into three groups: clade I and clade II gene members being orthologues of ATTIR1/AFB1 and ATAFB2/AFB3. All of those proteins contain FBOX and leucine rich repeat domain. The clade III gene members were orthologues of ATAFB4/AFB5, containing low complexity structure. The transcriptome dada showed that some of soybean auxin receptors performed tissue specific expression patterns, indicating that those genes may function in related development stage. Histochemical staining results showed that some of the soybean auxin receptors expressed specifically in root tips and lateral root primordia, suggesting the important roles of those genes in regulation of soybean main root development and lateral root growth.
To explore the role of GmWRI1 transcription factors in regulating oil development in soybean, GmWRI1 gene was cloned from seeds of Jiyu 72 at the 35th day after flowering, and its deduced protein’ properties, structure and function were preliminary analyzed. To characterize the expression pattern of GmWRI1 at different stages after flowering,seeds of Jiyu 72 were also detected by real-time quantitative PCR. The results showed that the expression level of GmWRI1 may correlate with the soybean seeds oil content. Furthermore, pGBKT7-GmWRI1 as expression vector was constructed using recombinant DNA technology and expressed in yeast (AH109) to analyze its transcriptional activation ability. The results showed that GmWRI1 had transcriptional activation ability in yeast, which suggested that it was a transcription activator.
To understand glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT; EC2.3.1.15) gene under abiotic stress, we cloned BnGPAT9 gene (GenBank: KX344511.1) of B. napus. Sequence analysis showed that the gene was 1 131bp long, encoding 376 amino acids. Homology analysis showed that BnGPAT9 protein was highly homologous to other GPAT9 proteins from different plants, and was highly conserved in the process of biological evolution. qRT-PCR results showed that BnGPAT9 expressed specially in 1-4 week-seeds after flowering and in the stem, flower, leaf, root and silique wall. Abiotic stress (at 5-6 leaf stage) results showed that the expression of BnGPAT9 was enhanced by PEG-drought and high temperature, but was inhibited by low temperature, 6-BA, ABA and salt. Z pattern was found under waterlogging. The expression reached the lowest at 12h, and returned at 24h.
Ecological shuttle breeding method was summarized in Brassica napus breeding for early mature, wide adaptability and high oil content. Breeding was carried out between 2 sites in winter (at Dali, Shaanxi Province) and spring (at Zhangye, Gansu Province). Consecutive program spanned from 2001 to 2013. Results showed that average oil content was improved, and was higher in Zhangye. In 2013, one line with super-high oil content was obtained with 63.8% oil in seeds. During these years, registered cultivars with high oil content and/or shorter growth period were bred by the shuttle method. For the winter-type rapeseed, the plant adaptability in spring area was also obtained. Some of the CMS lines had the ecological male sterile feature, which facilitated higher efficiency of hybrid seed production. By using the variance of ecological areas and by consecutive artificial selection, excellent materials could be bred by this method. It had special advantages for creating germplasm with high oil content, early mature, wide adaptability and other excellent agronomic traits in B. napus, especially by using “high oil content germplasm + chemical hybridizing agents” model for high heterosis breeding.
in order to alleviate waterlogging stress and promote rapeseed (Brassica nuapus L.) growth, effects of strigolactones on root-shoot biomass and physiological traits were investigated. In pot experiments, Zhongshuang 11 seedlings at 5-leaf stage were waterlogged for 7d. Then both seedlings from waterlogged group and control group were root-irrigated by strigolactones (SL) in 4 concentrations (0, 0.1, 1 and 5μmol/L).The root and shoot growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme were investigated at 3d and 7d after strigolactones treatments respectively. Results showed that both the root and shoot dry weight increased significantly after 1μmol/L SL treatment for 3d and 7d in waterlogged group. The net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs) and transpiration rate (Tr) were significantly increased, while the intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) decreased. The relative electron transfer efficiency (rETR), PSⅡmaximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), PSⅡpotential activity (Fv/Fo), PSⅡeffective quantum yield (Fv'/Fm') and PSⅡactual energy conversion efficiency (ФPSⅡ) increased, but nonphotochemical quenching efficiency (qN) decreased. Meanwhile, leaf chlorophyll, POD and CAT activities increased, whereas SOD activity decreased. The results showed that 1μmol/L SL effectively alleviated the waterlogging stress. It promoted seedlings growth by increasing biomass, photosynthetic efficiency, photosynthetic pigment content, and reducing non-photochemical quenching and SOD activity.
Jidou 21, Jidou 12, Hedou21 and Qihuang 34 were selected in this paper, aiming to further spreading the extension and utilization of high protein soybean in China. Through the study of economic characters such as plant growth, dry matter accumulation, the quality and yield of high protein soybean with different density, the results showed that with the increasing density, the plant height and nod numbers of stem both increased, but the effective braches, effective pods, grains per pod and pod length of single plant all decreased. Similarly, with the increase of density, the dry matter accumulation of single plant reduced, but the group dry matter accumulation increased initially and then decreased. In the density of 22.5×104 to 25.5×104 plants·hm-2, the protein content of high protein soybean slightly increased with the increase of density, while the total fat content slightly decreased. The yield of soybean exhibited parabolically trend increase with the density, the best yield of Jidou 21 and Jidou 12 were the density of 22.5×104 plants·hm-2~ 25.5×104 plants·hm-2 , and the best yield of Hedou21 and Qihuang 34 were the density of 19.5×104 plants·hm-2~ 22.5×104 plants·hm-2. The results showed that the suitable density benefited the plant growth and type building of high protein soybean, then promoted the accumulation and allocation of dry matter, increased the grain yield eventually. This study provided a base for the extension and utilization high protein soybean in Huang-Huai-Hai region.
Cultivation experiments in high yield loam were conducted to study the effects of spraying oligochitosan on leaf senescence, pod yield and kernel quality with Huayu 20 (HY20) and Huayu 25 (HY25) as the materials. 4 oligochitosan concentrations were applied, they were T0 (0 mg·kg-1), T1 (50 mg·kg-1), T2 (100 mg·kg-1) and T3 (200 mg·kg-1) respectively. The results showed that spraying different concentrations of oligochitosan significantly improved chlorophyll content and SOD, POD, CAT activities, reduced the leaf content of MDA at pod filling stage. Spraying oligochitosan significantly increased the pod yield by improving the pod number per plant and pod filling rate. Different concentrations of oligochitosan all improved the fat content but slightly reduced the protein content of both these two cultivars, meanwhile, these treatments improved O/L value of HY20 but reduced the value of HY25. These two cultivars obtained the highest yield, protein and fat content when the concentration of oligochitosan was 100 mg·kg-1, which assisted in achieving high-yield, high-quality and high-efficacy of peanut production.
The objective of this study was to investigate response of different peanut varieties to acid stress, and to screen acid tolerant varieties and evaluation indexes, which provided sources for breeding acid-resisting peanut varieties and acid-resisting evaluate of massive varieties. Subordination function method and clustering analysis were used to evaluate the acid tolerance of 42 genotypes based on their agronomic characteristics, fresh and dry weight of each organ, leaf photosynthetic characteristics and root morphology in soils of pH3.5 and pH6 under pot condition. Principal component analysis and correlation analysis were used for screening acid resistance evaluation indicators of peanut seedlings. The result showed that, 26 single indexes could be classified into 6 independent comprehensive components, which reflected 85.57% information of all traits information. The first 3 comprehensive components had great effect on acid resistance, which could be summarized as root morphology with thin and medium diameter and biomass factor, canopy shape and biomass factor, and root morphology factor with thick diameter. And the cumulative contribution rate of the first 3 comprehensive components was 73.08%. The later 3 components had less effect on acid resistance, which could be summarized as photosynthetic factor. (2) The comprehensive acid tolerance values (D) were calculated from the subordination function method. And based on Euclidean distance 5, 42 peanut varieties were divided into 4 acid tolerance types by cluster analysis. 7 varieties, including Rihua 1 etc., were of highly acid resistant type and the D value of them were 0.645-0.771. 19 varieties (PD609, etc.) were of medium acid resistant type, and D value of which were 0.479-0.595. 14 varieties, including Zhongkai 1 etc., were of acid sensitive type, and D value of which were 0.299-0.460. In addition, Huayu 28 and Huayu 33 belonged to acid sensitive type, and D value of which were 0.098-0.212. (3) Fresh and dry weight of root, stem, leaf, whole plan, root length, volume and superficial area of diameter 0-1mm, 1-2mm and whole roots, and leaf area had highly significant positive correlations with acid tolerance values. Moreover, seeding speed, root length, volume and superficial area of diameter ≥2mm had significant positive correlations with acid tolerance values. Fresh and dry weight of root, stem, leaf, whole plant and leaf area could be used for rapid authenticating acid resistance of peanut seedlings. However, root morphology indexes of different diameters could be used as auxiliary determinative index.
In order to identify the proper soil tightness for peanut pod growth and development, different soil bulk density treatments were designed by using soil column cultivation method, the effects of different soil tightness on pod growth of peanut were studied. The results showed that too high bulk density of soil was not conducive to the formation and drilling in the soil of peanut needles, pod enlargement and dry matter accumulation during the whole peanut growth period. Although soil bulk density was beneficial to the formation and drilling in the soil of peanut needles, pod enlargement and dry matter accumulation in the early growth period, but it was not conducive to the formation and drilling in the soil of peanut needles and small pods growing to large ones in the middle and late stage. Both too high or too low soil bulk density could reduce the number of medium and large pods, and result more small pods, less dry matter accumulation in the late growth stage. The suitable soil bulk density (1.2-1.3g/cm3) was beneficial to the formation and drilling in the soil of peanut needles, pod enlargement and dry matter accumulation in the whole growth period of peanut. In the late mature period, it would form more medium and large pods with greater dry matter accumulation and fewer small pods.
to improve autumn sesame yield, quality and nitrogen use efficiency on upland red soil, field trails were carried out to study the effects of nitrogen and plant density on autumn sesame. Sesame cultivar Ganzhi 5 was used under 3 density (D1 2.25×105, D2 3.00×105, D3 3.75×105 plants per hectare) and 4 nitrogen levels (N0 0, N1 52.5, N2 105.0, N3 157.5 kg per hectare) at Dongxiang and Jinxian counties of Jiangxi Province in 2014 and 2015 respectively. Results indicated that yield of D2 and D3 were increased by 49.82% and 76.53% (compared to N0) under N2 in 2014 and 2015 respectively. Yield of D3 was significantly increased by 18.44% (compared to D1) in 2014, but was significantly reduced by 12.35% (compared to D1) in 2015. As nitrogen fertilizer usage increased, sesame oil content increased first, then decreased; protein content increased, and sesamin content reduced significantly by 17.8-20.0%. As density increased, sesame capsule number per plant and 1000-seed weight reduced. Nitrogen agronomy efficiency and partial factor productivity efficiency maintained at 3.29-4.84 and 9.89-11.17 kg/kg under N2 treatment. In conclusion, D1 was optimum in Jinxian, D3 was optimum in Dongxiang. And N2 was optimum to all upland red soil.
To simplify the rapeseed cultivation, simultaneous operation of seed sowing and boron fertilizer application was studied in field using 2 cultivars (Huayouza 9 and Huayouza 62) of Brassica napus L. The results showed that simultaneous sowing of rapeseeds and boron fertilizer had no negative effect on seed emergence under the normal boron application. The emergence rate were all over 80% with both H9 and H62. Compared with control, simultaneous operation increased 3.3-13.3 (H9, Huayouza 9) and 1.7-15.3 (H62, Huayouza 62) percentage points on the emergence rate respectively. The proper amount of boron was between 4.5 to 9.0 kg·hm-2. Moreover, simultaneous operation promoted seedling growth. Boron 13.5kg·hm-2 led to the highest yield. By equation fitting, the optimum boron amounts were 13.4 kg·hm-2 and 10.1 kg·hm-2 to H9 and H62 respectively. Boron utilization efficiency was also improved. Under 13.5 kg·hm-2 boron fertilizer, H9 had higher use efficiency (26.5%) than that of H62 (23.1%). These results indicated that the simultaneous method could be used in rapeseed production. Under boron starvation (≤0.25 mg·kg-1) area, the recommendation boron fertilization rate was 10-13.5 kg·hm-2).
To explore the effects of nitrogen (N) application time on plant biomass and N accumulation, N utilization efficiency, and peanut yield in red soil upland, a field randomized block experiment, with Yueyou 256 as the test material, was carried out in this study. There were 6 treatments, which were no N fertilizer (CK), 100% N basal application (N10:0:0, local traditional N application method), 70% N basal application and 30% N topdressing at flowering stage (N7:3:0), 50% N basal application and 50% N topdressing at flowering stage (N5:5:0), 50% N basal application and 30% N topdressing at flowering stage and 20% N topdressing at pod setting stage (N5:3:2), and 30% N basal application and 50% N topdressing at flowering stage and 20% N topdressing at pod setting stage (N3:5:2). The results showed that plant biomass and N accumulation among all treatments could be described by Logistic equation, and their accumulation characteristics were significantly affected by N application time. Split application and appropriate delay could significantly accelerate the maximal speed of biomass and N accumulation (vmax); the maximal speed (tmax) would be postponed and the duration of rapid accumulation (?t) would be prolonged. Therefore, the N utilization efficiency and peanut yield significantly improved. But it was negative for N efficiency when a large proportion of N application was delayed (N3:5:2). In this study, the peanut yield reached maximum under N5:3:2 treatment (4 918.5 kg·hm-2), which increased 20.0% and 9.8% compared to CK and local traditional N application method (N10:0:0) respectively. In conclusion, reasonable N application time was an effective way to increase peanut yield and N utilization efficiency. This study could provide theoretical support for scientific and rational fertilization and high yield and high efficiency cultivation of peanut in red soil upland in South China.
To study the effects of Ca, Mo and B fertilizer combined application on growth, development, yield and kernel quality of peanut, plant morphological characters, dry matter accumulation, yield and quality characters of peanut variety Nonghua 5 were investigated after application of medium and micro fertilizers in field experiments in 2013 and 2014. The results showed that additional application of Ca (T1) and Ca+Mo (T2) could promote the growth of Nonghua 5 with improved main stem height, lateral branch length, leaf area per plant, dry matter accumulation for organs, 100-pod weight, 100-kernel weight and full pod number per plant, which eventually improved the pod yield. T2 treatment had a better effect with a yield of 6 438.24kg/hm2 and 6 015.47kg/hm2 each year respectively, which was an increase of 13.6% and 6.9% compared with control. Ca+Mo+B (T3) had a resistant effect with a yield decrease of 3.65% and 14.77%. Adding medium and micro fertilizers could improve peanut kernel quantity which improved crude fat and protein content in the kernels, and at the same time a decrease of soluble sugar content. The most significant treatment was T2, then T1, and there was no significant effect for T3 treatment. This study provided a guideline for fertilizer application of Ca and Mo and B in main peanut producing area of Liaoning Province.
To better understand cabbage resisitance and gene loci on clubroot disease, clubroot resistance (CR) of 28 Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.) were evaluated in green house. The clubroot pathgen (Plasmodiophora brassicae) samples were collected from 8 different locations, including the main races in the major production areas of rapeseed (race 2, 4 and 13) and strains from Enshi, Deyang, Tangshan and Nanyang. CR loci (Crr1, Crr2, Crr3, CRa, CRb, CRc and CRk) were detected using 7 reported CR markers. Results indicated that 27 cultivars showed resistance to some strains, while Genwang F1 was susceptible to all strains. The best 10 cultivars (including CR Chunfu) showed resistance to all strains. 12 cultivars were susceptibile to only 1 strain, 9 of which was susceptible to the strain from Enshi. CRk were detected commonly in resistant cultivars. Crr3 hybrid resistant locus was detected only in CR Chunfu. No CR loci were found in susceptible cultivar Genwang F1. In general, cultivars with more CR loci resisted to more strains. The exception was that one cultivar had 4 loci, but was susceptible to most of the strains (e.g. 4 CR loci in CR-huangxin F1 were susceptible to race 2, 4 and 13). And, the other exceptional cultivar had 1 locus but resisted to all strains (e.g. only one locus CRk was detected in Degao CR117 and Rongyao which showed resistance to all strains). It suggested the complexity of cabbage resistance to clubroot
In this study, 6 exogenous soybean isoflavones, including daidzein, daidzin, genistein, genistin, glycitin and glycitein, were selected to identify the inhibition efficiency on Heterodera glycines. Nematicidal efficacy of these isoflavones was investigated through inhibition of egg hatching and mortality of second-stage juveniles (J2). In addition, field efficiency trials of seeds soaked with isoflavones were determined. The results showed that all 6 isoflavones could inhibit H. glycines to some extent, and genistein had the highest mortality of 45.46% on J2 and inhibition rate of 43.48% on egg hatching at concentration of 100 μg/mL after 24 h treatment, also had inhibition rate of 49.47% at concentration of 50 μg/mL in field trials. Genistin and daidzein significantly killed J2 and inhibited egg hatching, but their control efficacies were weaker than those of others in field trials.
¬¬¬¬Glycitin and glycitein had weaker toxicity on J2 and higher inhibition on egg hatching than genistin and daidzein. Furthermore, daidzin showed the weakest inhibition of J2 and egg hatching than other 5 isoflavones in vitro in plant nematology laboratory, but its control efficacy in the field showed no significant differences compared with genistein. The research confirmed that soybean isoflavones had positive suppressive ability on H. glycines, especially genistein, showed better comprehensive efficacy. The results suggested that isoflavones played an important role in resistance mechanism of soybean against nematode infection, and also provided clues in control soybean cyst nematode by soybean isoflavones.
Plasmodiophora brassicae is an important disease in rapeseed production. For better control, inhibition of 4 fungicides (fluazinam, oxine-copper, quintozene and carbendazim) against P. brassicae were detected with spore germination and pot experiments. Results showed that of fluazinam (5.5mg/L) had the strongest inhibition on P. brassicae spore germination with inhibition rate of 38.1%, which was significantly higher than that of others. Oxine-copper, quintozene and carbendazim had 9.5-15.0% inhibition rates, with no significant difference among them. In pot experiments, fluazinam (5.5mg/L) also had the strongest effects (86.1%) under root irrigation, which was significantly higher than that of others. Oxine-copper (0.62mg/L) had the efficacy of 73.2%. Quintozene and carbendazim had low effects. Among the 4 fungicides, defense enzyme activities of PAL (phenylalanine ammonialyase), POD (peroxidase) and PPO (polyphenol oxidase) were much higher in seedlings treated by 5.5mg/L fluazinam. Therefore, the efficacy of fluazinam on P. brassicae was worthy of further research in rapeseed production.
AFLP protein is a key enzyme in the late period of aflatoxin synthesis. SUMO-AFLP fusion protein expressed by Escherichia coli was used as immunogen to immunize Balb / c mice. Spleen cells of positive serum mice were selected and fused with SP2 / 0 myeloma cells. Monoclonal hybridoma cells were screened by indirect ELISA and limited dilution. Thus the hybridoma cell lines were screened with stable secretion of anti-AFLP monoclonal antibody. Ascites antibodies were induced and prepared by the positive cell line, and were purified by caprylic acid / ammonium sulfate precipitation. By indirect ELISA and Western blotting, one hybridoma cell line 3B4 3B10 was found which could secret the anti-AFLP monoclonal antibody, and the subtype was IgG2a. The antibody ascites iter was 1:256 000. Western blotting showed that the anti-AFLP monoclonal antibody specifically recognized both recombinant and native AFLP proteins in Aspergillus flavus. By 1 μg·mL-1 monoclonal antibody detection, the linear range was 1.259 - 57.335 ng·mL-1 with the limit of 0.851 ng·mL-1 (R2 = 0.998 3). In conclusion, monoclonal antibody against native AFLP protein was successfully prepared with high specificity and sensitivity, which laid foundation for further study in AFLP expression and functional mechanism.
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is one of important crops in southern China. This paper summarised peanut breeding in southern China during last decade, analyzed the trend of peanut production and uncovered the main factors affecting peanut production in southern China. According to the regional trial data of varieties in last decade, we analyzed the current situation and the main problems of peanut breeding in southern China in the aspects of yield, plant type, pod, disease resistance and quality traits. The results indicated that breeding methods and hybrid parents were more important determinants in breeding programs. Some practicable suggestions were made to guide the genetic improvement of peanut breeding in southern China in future.
Glyceroglycolipid is a crucial component of plant cell membrane. It has a complex structure for binding fatty acids on its skeleton, which leads to difficulty on glyceroglycolipid analysis. This paper reviewed several aspects concerning glyceroglycolipid, including structure and biological function, extraction and separation methods, mass spectrometry identification and quantitative analysis methods and applications in lipidomics. Furthermore, the possible development in future was also prospected to provide references in establishing analysis methods for glyceroglycolipid biological functions.